Your Source for Children’s Dentist Info
Do I need to bring my child to dentist? When should we go?
Why worry about my child’s baby teeth?
They are going to fall out anyway! 1
Potential problems if a child does not see a children’s dentist.
37%
of 2-8 year olds have tooth decay or
cavities in their baby teeth. 1

Research shows a child’s poor oral health is due to lack of knowledge and poor attitudes of caregivers about the importance of oral healthcare.2
Many caregivers believe dental issues
should only be responded to only when
there is pain or visible cavities.3

Childhood dental issues are preventable
with regular preventive dental care and appropriate
oral hygiene habits.4

ONLY
1 IN 5

Fewer than 1 in 5 caregivers seek follow-up dental care for their
children, even when a dental screening shows a need. 5
Untreated tooth decay and cavities in adolescents are
a significant indicator of future issues
due to continued decay. 6

An individual will spend nearly $60,000 on their
dental health over the course of a lifetime.7
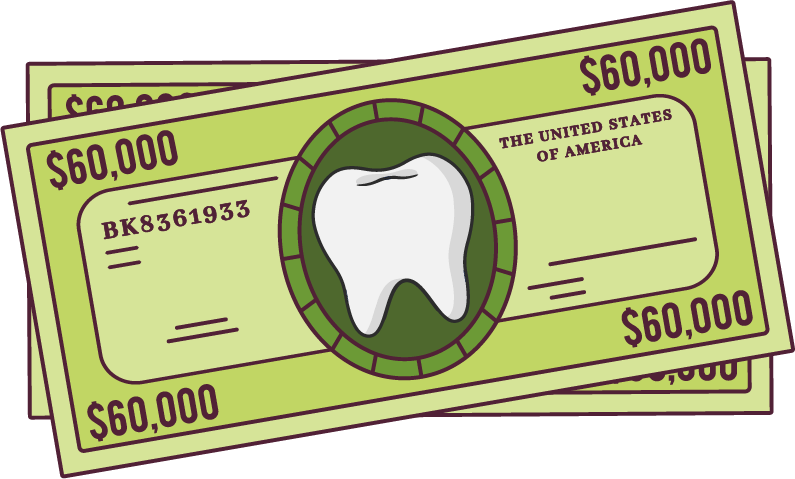

This amount can increase with poor dental care.
WHY SEE A CHILDREN’S DENTIST?
Better Health. Lower Costs.
Good oral health starts early. Creating healthy habits with regular check ups at the dentist reduces dental issues and long-term costs for care. Seeing a pediatric dentist that is specially trained on caring for kids can only make things better.
A healthy smile is a beautiful smile!
Topics to explore related to Children’s Dentistry
Why Choose a Children’s Dentist?
A children’s dentist is specifically trained to handle the unique dental needs of infants, children, and adolescents.
Here are a couple great reasons to choose a children’s dentist:
- Specialized Training: Pediatric dentists complete specialized training focused on child psychology and techniques for treating children.
- Child-Friendly Environment: Kids dental offices are designed to be welcoming to children.

What’s the reason to go to a Children’s Dentist?
A children’s dentist plays a crucial role in ensuring the oral health and well-being of children from infancy to adolescence, including:
- Preventive Care: regular check-ups, cleanings, fluoride treatments, and dental sealants help protect against cavities.
- Education: Pediatric Dentists help parents and children understand hygiene practices, diet, and habits that can impact oral health.
- Treatment of Dental Issues: treatment of cavities, gum disease, and tooth decay can prevent emergencies and higher costs later.
- Behavior Management: it is important to reduce fear of the dentist early, and kid dentists are specially trained to use positive reinforcement and distraction to help create a welcoming experience.
Brought to you by

1 Dye BA, Thornton-Evans G, Li X, Iafolla TJ. Dental caries and sealant prevalence in children and adolescents in the United States, 2011-2012. Hyattsville, MD: National Center for Health Statistics; 2015. NCHS data brief, no 191.
2 Featherstone JD, Adair SM, Anderson MH, Berkowitz RJ, Bird WF, Crall JJ, Den Besten PK, Donly KJ, Glassman P, Milgrom P, Roth JR, Snow R, Stewart RE. Caries management by risk assessment: consensus statement, April 2002. J Calif Dent Assoc. 2003. Mar;31(3):257-69. PMID: 12693825.
3 Hooley M, Skouteris H, Boganin C, Satur J, Kilpatrick N. Parental influence and the development of dental caries in children aged 0-6 years: a systematic review of the literature. J Dent. 2012;40:873–885.
4 American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry. Guideline on periodicity of examination, preventive dental services, anticipatory guidance/counseling, and oral treatment for infants, children, and adolescents. Pediatr Dent. 2013;35(5):E148–E156.
5 Nelson S, Mandelaris J, Ferretti G, Heima M, Spiekerman C, Milgrom P. School screening and parental reminders in increasing dental care for children in need: a retrospective cohort study. J Public Health Dent. 2012;72:45–52.
6 Motohashi M, Yamada H, Genkai F, Kato H, Imai T, Sato S, et al. Employing dmft score as a risk predictor for caries development in the permanent teeth in Japanese primary school girls. J Oral Sci. 2006;48(4):233–237
7 [using study based on Blue Cross Blue Shield data and inflated to 2024 dollars] Alemayehu, B., & Warner, K. E. (2004). The lifetime distribution of health care costs. Health Services Research, 39(3), 627–642. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1475-6773.2004.00248.x


